Service Hotline
As electronic devices continue to shrink while offering more functionality, efficient PCB interconnection has become a critical design challenge. Board-to-Board connectors provide a reliable solution for directly connecting two printed circuit boards without using cables, helping designers save space, simplify assembly, and improve signal integrity.
In this article, we explore the main types of board-to-board connectors, their applications, key design considerations, and how to select the right solution for your project.
1. Introduction to Board-to-Board Connectors

A Board-to-Board connector is designed to electrically and mechanically connect two PCBs together. Unlike wire-based connections, these connectors enable direct board-level interconnection, making them ideal for compact, modular, and high-density electronic designs.
They are widely used in consumer electronics, industrial systems, automotive electronics, and communication equipment, where reliability, alignment accuracy, and space efficiency are essential.
2. Common Types of Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-Board connectors come in several structural forms, each optimized for different layout requirements:
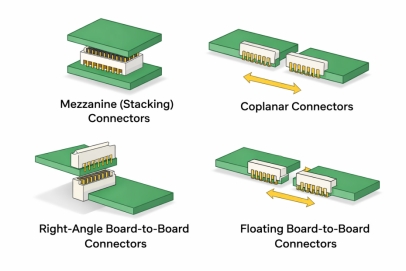
l Mezzanine (Stacking) Connectors
Mezzanine connectors stack two PCBs vertically, creating a compact multi-layer structure. They are commonly used in smartphones, embedded systems, and IoT devices where height control and high pin density are critical.
l Coplanar Connectors
Coplanar connectors connect two boards on the same horizontal plane. This design is useful when boards need to be extended or aligned side by side without increasing product height.
l Right-Angle Board-to-Board Connectors
These connectors link PCBs at a 90-degree angle, making them suitable for enclosures with limited depth or L-shaped internal layouts.
l Floating Board-to-Board Connectors
Floating connectors allow a certain degree of misalignment between boards, helping reduce assembly stress and improve long-term reliability—especially in industrial and automotive applications.
3. Key Design Features and Specifications
When selecting a Board-to-Board connector, several technical parameters should be carefully evaluated:
l Pin Pitch and Board Spacing
Smaller pitch connectors enable higher density but require tighter PCB tolerances. Board spacing determines the connector height and affects airflow and mechanical stability.
l Contact Structure and Plating
High-quality contact materials and surface plating (such as gold) help reduce contact resistance and improve durability over repeated mating cycles.
l Current and Voltage Ratings
Ensure the connector can safely handle the required electrical load, especially in power distribution or mixed signal-power designs.
l Signal Integrity
For high-speed data transmission, connector design plays a key role in minimizing signal loss, crosstalk, and impedance mismatch.
4. Applications of Board-to-Board Connectors
Board-to-Board connectors are widely used across multiple industries:
l Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, tablets, cameras, and wearables rely on compact board-to-board connections to maximize functionality in limited space.
l Industrial Control and Automation
These connectors enable modular system design in PLCs, control boards, and industrial computers.
l Automotive Electronics
Used in infotainment systems, ADAS modules, and control units, where vibration resistance and reliability are critical.
l Medical and Communication Equipment
Precision and stability are essential in medical devices and communication systems, making board-to-board connectors a trusted solution.
5. How to Choose the Right Board-to-Board Connector
Choosing the right connector requires balancing mechanical, electrical, and environmental factors:
l Mechanical Alignment and Tolerance
Floating or guided connectors can help accommodate assembly tolerances and reduce stress during installation.
l PCB Layout and Assembly Method
Consider whether the connector supports surface-mount or through-hole assembly and matches your production process.
l Space-Saving vs. Robustness
Ultra-fine pitch connectors save space but may require more precise assembly, while larger pitch designs offer greater mechanical strength.
l Environmental Requirements
Temperature range, vibration, and humidity resistance should match the application environment.
6. Kinghelm Board-to-Board Connector Solutions
Kinghelm offers a range of Board-to-Board connector solutions designed to meet the demands of modern electronics. Our connectors emphasize:
l Rugged mechanical design for long-term reliability
l Stable electrical performance with consistent contact quality
l Compact structures suitable for high-density PCB layouts
l Compliance with international standards, including RoHS
With years of experience in connector manufacturing, Kinghelm supports customers across consumer, industrial, automotive, and communication markets.
7. Conclusion
Board-to-Board connectors are a key enabler of compact, modular, and high-performance electronic designs. By understanding connector types, specifications, and application requirements, engineers can select solutions that improve reliability and simplify system architecture.
Kinghelm remains committed to delivering dependable board-to-board connectivity solutions that support efficient PCB design and long product life.